Sertraline FAQ
 Sertraline is one of the most widely prescribed antidepressants worldwide and among the most commonly used SSRIs in everyday psychiatric practice in India. It was approved for medical use in the early 1990s and has since been studied extensively across a wide range of conditions, age groups, and clinical settings.
Sertraline is one of the most widely prescribed antidepressants worldwide and among the most commonly used SSRIs in everyday psychiatric practice in India. It was approved for medical use in the early 1990s and has since been studied extensively across a wide range of conditions, age groups, and clinical settings.
Its popularity comes from a balance of effectiveness, safety, and flexibility. Sertraline works well for both depression and anxiety disorders, can be used across a broad dose range, and is often preferred when anxiety, panic, obsessive thoughts, or trauma-related symptoms are prominent.
In India, sertraline is available under many familiar brand names such as Zoloft (original), Serlift, Serta, Zosert, Daxid, and others. While brand names differ, the active medicine is the same, and outcomes depend far more on correct dosing, consistency, and follow-up than on the specific brand chosen.
Introduction
Being advised to start sertraline often raises a familiar set of questions.
Some people worry about side effects. Others are concerned about long-term use, emotional numbing, or whether they will become dependent on the medication. Many have already read conflicting information online, which can increase anxiety rather than reduce it.
These concerns are understandable.
Sertraline is neither a “strong drug” that needs to be feared, nor a casual pill to be taken without thought. Like all psychiatric medications, it works best when prescribed carefully, monitored properly, and understood clearly.
This article is meant to provide that clarity.
The aim is not to persuade you to take sertraline, but to help you understand what it does, what it does not do, what is common, what is rare, and how it is usually used thoughtfully in real clinical practice.
What does sertraline do?
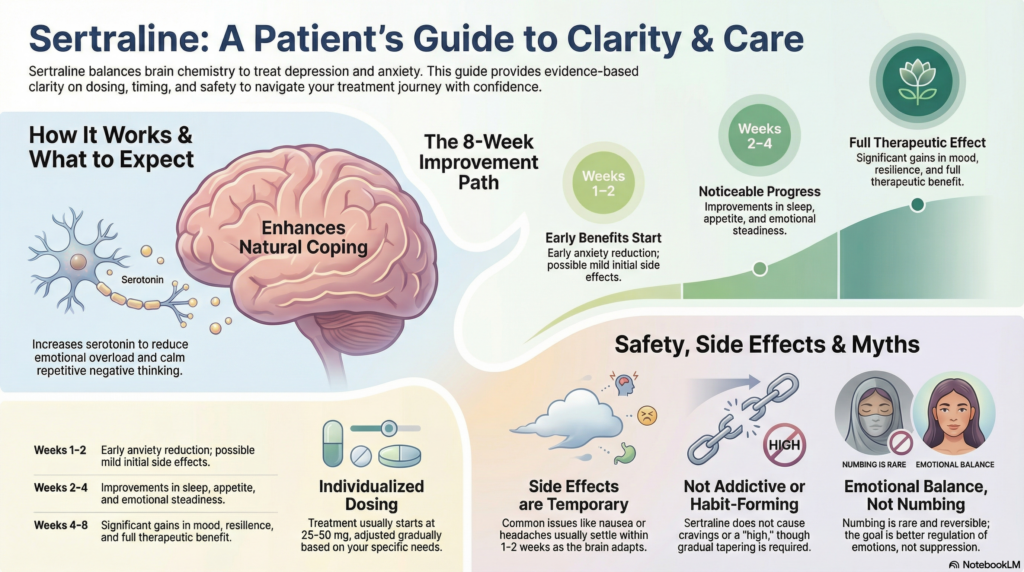
Sertraline belongs to a group of medications called SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors).
In simple terms, it:
-
Increases the availability of serotonin, a chemical involved in mood regulation, anxiety control, and emotional balance
-
Reduces excessive fear responses and emotional reactivity
-
Helps calm repetitive negative thinking and rumination
Sertraline does not create artificial happiness or suppress emotions.
It helps reduce emotional overload so that your natural coping abilities work more effectively.
Sertraline is commonly prescribed for:
-
Depression
-
Generalised anxiety disorder
-
Panic disorder
-
Social anxiety disorder
-
Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD)
-
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
What is the usual dose range of sertraline?
Dosing is individualised and adjusted gradually.
Typical ranges:
-
Starting dose: 25–50 mg once daily
-
Common effective dose: 50–150 mg once daily
-
Maximum dose: 200 mg per day
Many people—especially those with anxiety—do well with slow dose increases. Higher doses are not always necessary and are used only when benefits clearly outweigh side effects.
Should sertraline be taken with food or after food?
Sertraline can be taken with or without food.
However:
-
If nausea or gastric discomfort occurs, taking it after food often helps
-
Food does not reduce its effectiveness
-
Taking it at the same time every day improves tolerability
Does sertraline make you sleepy or drowsy?
This varies between individuals.
-
Some people feel slightly sleepy or relaxed, especially early on
-
Others feel mildly alert or activated
-
Most people feel neutral after the first few weeks
If it causes sleepiness:
-
Taking it at night may help
If it causes alertness or restlessness:
-
Morning dosing is usually better
This is a timing issue, not a dangerous side effect.
How long does sertraline take to work?
Sertraline works gradually, not immediately.
-
Week 1–2: Early side effects or mild anxiety reduction may appear
-
Week 2–4: Sleep, appetite, and emotional steadiness often improve
-
Week 4–6: Mood, confidence, and resilience improve
-
Week 6–8: Full therapeutic benefit usually becomes clear
Early lack of improvement does not mean the medication will not work.
Does sertraline make you emotionally numb?
This is a common concern.
Most people experience:
-
Less emotional overwhelm
-
Better regulation of emotions
-
Improved ability to cope with stress
A small minority, particularly at higher doses, may experience:
-
Emotional blunting
-
Feeling “flat” or less reactive
Important points:
-
This effect is dose-related
-
It is reversible
-
Dose adjustment or medication change usually resolves it
Emotional numbness is not the goal of treatment.
What are the common side effects?
Most side effects are mild and temporary, especially in the first 1–2 weeks.
Common:
-
Nausea or loose stools
-
Headache
-
Fatigue or mild restlessness
-
Sleep changes
-
Reduced libido or delayed ejaculation (in some people)
Less common:
-
Jaw tightness
-
Sweating
-
Brief increase in anxiety at the start
Most side effects settle as the brain adapts.
Does sertraline cause dependence or addiction?
No.
Sertraline does not:
-
Cause cravings
-
Produce a “high”
-
Lead to drug-seeking behaviour
-
Require increasing doses to feel normal
Needing to taper slowly does not mean addiction.
Will I have withdrawal symptoms if I stop sertraline abruptly?
Stopping suddenly can cause discontinuation symptoms, especially after long-term use.
Possible symptoms include:
-
Dizziness
-
Head heaviness or “electric shock” sensations
-
Irritability or anxiety
-
Sleep disturbance
-
Flu-like feelings
This occurs due to sudden serotonin system changes, not addiction.
To avoid this:
-
Sertraline should be tapered gradually
-
Taper schedules depend on dose and duration
-
Most people stop comfortably with guidance
What is the risk of PSSD (Post-SSRI Sexual Dysfunction)?
PSSD refers to persistent sexual symptoms after stopping SSRIs.
Key points:
-
PSSD appears to be rare
-
Most sexual side effects improve after dose reduction or stopping
-
The majority of patients recover fully
-
Risk may be higher with long-term high-dose use, but remains uncommon
Sexual function is influenced by many factors:
-
Depression and anxiety themselves
-
Stress and fatigue
-
Sleep quality
-
Hormonal factors
-
Relationship issues
Open discussion allows early management.
Are there alternatives to sertraline?
Yes. Sertraline is one option among many.
Alternatives may include:
-
Other SSRIs
-
SNRIs
-
Atypical antidepressants
-
Psychological therapies
-
Sleep-focused interventions
-
Combined approaches
Medication choice depends on the individual, not just the diagnosis.
Is sertraline safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
This requires an individualised risk–benefit discussion.
-
Sertraline is among the most commonly used SSRIs during pregnancy and breastfeeding when clinically necessary
-
Untreated depression or anxiety also carries risks
-
Decisions depend on symptom severity, history, and alternatives
Never stop medication suddenly during pregnancy without medical advice.
How long will I need to take sertraline?
This varies:
-
First episode: usually 6–12 months after recovery
-
Recurrent depression or anxiety disorders: sometimes longer
Stopping medication is always a planned, gradual process.
Final thoughts
Sertraline is a well-studied, reliable medication when used for the right reasons and in the right way.
Good psychiatric care is not about avoiding medication at all costs.
It is about using the right tool, at the right dose, for the right duration, with understanding and follow-up.
Clear understanding reduces fear—and fear reduction itself supports recovery.
About the author
Dr. Srinivas Rajkumar T, MD (AIIMS), DNB, MBA (BITS Pilani)
Consultant Psychiatrist & Neurofeedback Specialist
Mind & Memory Clinic – Apollo Clinic Velachery (Opp. Phoenix Mall)
I provide evidence-based psychiatric care integrating medication, psychotherapy, sleep science, and modern neuropsychiatry—tailored to each individual.
✉ srinivasaiims@gmail.com
📞 +91-8595155808